2019-06-18 14:02:22 XinHai Views:4093
Defination: Flotation reagent usually refers to a group of mining chemicals used to adjust the floatability of minerals in mineral froth flotation process, which can artificially increase the difference in wettability between various minerals, thereby achieving the separation of useful minerals and gangue minerals.
The flotation reagent is mainly classified into three types:
Flotation Collectors; Flotation Frothers; Flotation Conditioners.

Since most of the minerals in nature are hydrophilic, in order to achieve the purpose of mineral separation, it is necessary to artificially adjust the flotation behavior of ore. By adding flotation reagent, the concentrators can selectively increase the hydrophobic or hydrophilic of certain minerals, and cause the difference in wettability between different minerals, so that the useful minerals selectively adhere to the bubbles of the slurry and float to the surface of the slurry, and then be scraped off with the scraper to realize the enrichment of concentrate. The use of flotation reagent is currently the most flexible, effective, and convenient method of controlling flotation process.
| Categories | Types | Representative Flotation Reagent | Application Field | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flotation Collectors | Thiol (Thiocompounds) | Xanthate, Dithiophosphate, White Catching Agent | Flotation of Sulphide Ore | |
| Hydrocarbyl Oxyacids (Hydroxy) | Oleic Acid, Sodium Alkyl Sulfate | Flotation of Non-Sulphide Ore | ||
| Alkyl Amine | Mixed Amine | |||
| Hydrocarbon Oil | Kerosene, Light Diesel Oil | Flotation of Coal and Other Natural Hydrophobic Minerals | ||
| Flotation Foaming Agents | Alcohol Compounds | Terpenic Oil, MIBC | Flotation of Minerals and Coal | |
| Ether Alcohol Compounds | Ether Glycol Oil | Flotation of Minerals | ||
| Ketol Compounds | Diacetone Alcohol Oil | |||
| Oxane Compounds | Butyl Ether Oil | |||
| Flotation Conditioners | Activators | Various Metal Ions of Inorganic Salts | Cu 2+,Ca 2+ | Flotation of Minerals |
| Inhibitors | Organic Compounds and Inorganic Salts | Humic Acid,CN-,Hs | ||
| pH Conditioners | Acid, Alkali | H2SO4,NaOH | ||
| Dispersants | Inorganic Salts | Sodium Silicate, Na2C03 | ||
| Flocculants | Natural and Synthetic High-Molecular Compounds | Starch, Polyacrylamide | ||
| Defoamers | Inorganic Salts and High Fatty Acid Esters | Sodium Tripolyphosphate(STPP) | ||
Flotation Reagent Principles

The main function of the flotation collectors is to change the hydrophilicity of the mineral surface, enhance its hydrophobicity, and increase the adhesion of the mineral on the bubble, which can make it floatable and shorten the induction time.
Since most of the minerals in nature are hydrophilic, the flotation collector is widely used in flotation operations as a kind of flotation reagent. Generally, it can be divided into polar collectors and non-polar collectors. The commonly used collectors for flotation are mainly xanthate ,dithiophosphate and thiocarbanilide, etc.
The main function of the flotation frothers is to promote the formation of uniform bubbles and enhance the elasticity of the surface of the bubble. It can also make the bubbles generated by flotation more stable and not easily deformed. Even when subjected to vibration or other external force, bubbles are less likely to rupture. In addition, the stability of the foam is also affected by the pH of the pulp, the soluble salt content, etc. The commonly used flotation frothers are mainly pine oil ,methyl isobutyl carbinol (MIBC) and so on.
The main function of the flotation conditioners is to adjust the interaction between the collector and the mineral, adjust the pH of the slurry, and promote or inhibit the floatability of the mineral. According to the effect of the conditioners, it can be divided into the following categories:


Flotation Reagent Dosage

Froth flotation has certain requirements on the amount of flotation reagent dosage. Insufficient or excessive flotation reagents will affect the efficiency of mineral flotation.
If the collectors is insufficient, it will result in insufficient hydrophobicity of the useful minerals and reduce the recovery rate; if the collectors is excessive, the grade of concentrate will decrease.
If the flotation frothers is insufficient, the foam is poor in stability and easily broken; if the flotation frothers is excessive, "run slot" phenomenon may occur.
If the inhibitors is insufficient, the content of impurities in concentrate will increase; if the inhibitor is excessive, the mineral which should be floated will be inhibited and the flotation recovery rate will be reduced.
Due to the difference in properties of different ores, the fluctuation range of the flotation reagent dosage is different. Even for the same ore, the content of useful minerals and gangue minerals will be different. Therefore, in actual mineral flotation, a proper flotation reagent dosage needs to be determined according to the mineral dressing test. The dosage range of commonly used flotation reagents can be referred to the following data:
Flotation Collectors: 20-1500g/t,
Flotation Frothers: 20-2000g/t,
Flotation Activators: 200-1000g/t,
Flotation Inhibitors: 100-200g/t,
Medium conditioners: 500-3000g/t


Flotation Reagents Preparation Methods

There are many methods for preparing flotation reagents. With different preparation methods, the dosage and effect of the same flotation reagents are also very different. Proper preparation of flotation reagents before use will play an important role in improving the efficiency of the flotation reagent. Next, we will introduce 6 commonly used preparation methods of flotation reagents.
Most water-soluble flotation reagents can be formulated in this way and are typically formulated as 5% to 10% aqueous solutions. Flotation reagents using this preparation method include xanthate, copper sulfate, sodium silicate, and the like. When preparing an aqueous solution, we often dissolve the flotation reagent in the container with a small amount of water. When the dissolution of flotation reagent is finished, more water can be gradually added to reach the desired concentration.
For some flotation reagents that are insoluble or poorly soluble in water, a good preparing method is to dissolve them into some special solvent before use. For example, CS(NHC6H5)2 is insoluble in water, but is soluble in an aniline solution with a concentration of 10% to 20%. So it can be used after it is formulated into an aniline mixed solution.
For some non-soluble solid flotation reagents, it can be formulated into an emulsion. For example, the solubility of lime in water is very small. We can grind the lime into powder, and add water to make it into a milky suspension (such as calcium hydroxide). Or it can be directly added to the ball mill as dry powder.
For fatty acid collectors, saponification is the most common method. In order to improve the water solubility of the mixed flotation reagent, we can add about 10% of sodium carbonate to saponify the tall oil and heat the mixture with hot water to prepare a hot soap liquid when preparing the flotation reagent.
Some flotation reagents (such as pine oil, dithiophosphate 25, kerosene, etc.) have very low water solubility, and it is difficult to formulate a true solution or a stable emulsion. Instead of formulating it into a solution, it can be directly added into the ore pulp according to the dosage.
The aerosol method is a new preparation method that enhances the effect of flotation reagents. The essence of this method is to use a special spray device to directly add the flotation reagent to the flotation cell after the flotation reagent is atomized in the air medium. This method can not only improve the floatability of useful minerals, but also significantly reduce the dosage of flotation reagents.


Flotation Reagents Adding Location

The choice of the adding location of flotation reagents is usually related to the usage and solubility of the flotation reagents. In order to fully utilize the action of the flotation reagents, the selection of the addition location is usually the following.


Flotation Reagents Adding Methods

The way in which flotation reagents are added is usually divided into one-time additions and phased additions.
One-time addition means that all the flotation reagents are added to the slurry at one time before the flotation is carried out, which is beneficial to increase the initial speed of the flotation process and is also a convenient adding method. However, as the flotation process progresses, the flotation speed will slowly decrease. However, the overall flotation time is still short, which can improve the efficiency of flotation to a certain extent. The adding method of flotation reagents is mainly applicable to those flotation reagents which are easily soluble in water and which are not easily carried away by the foam, and which do not fail in the slurry due to the reaction, such as xanthate, sodium bicarbonate and lime.
Phased addition means that the flotation reagents is added to the slurry multiple times during the flotation process. Generally, 60%-70% of the total amount of flotation reagents is added before the flotation, and the remaining 30%-40% of the flotation reagents is added to the appropriate place during the flotation process. Such a flotation reagents addition method is beneficial to improve the quality of the concentrate. However, due to the low speed of the initial reaction during the flotation process, the entire flotation time will increase. Phased addition is mainly applicable to the following types of flotation reagents:


Flotation Reagents Application Cases

A copper-lead-zinc flotation processing plant in Xinjiang, China, decided to use preferential flotation process because of the close symbiotic relationship between copper and lead minerals in the ore. Firstly, a kind of flotation collectors with better selectivity is used as flotation reagent to preferentially float copper. After obtaining qualified copper concentrate, a suitable flotation reagent will be added for mixed flotation. The obtained mixed concentrate is regrind to improve the monomer dissociation degree of the copper-lead mineral and achieve the separation condition of the copper-lead mineral. The recovery rate of the final copper concentrate is 90.21%, and the recovery rate of lead concentrate is 88.3%. From this flotation project, we can see that targeted flotation reagents will help improve the flotation recovery rate.

Copper-Lead-Zinc Flotation Plant
The main minerals in a zinc-lead sulphide mine in South Africa are pyrite, galena, sphalerite, and gangue minerals are mainly quartz, calcite and dolomite. In the flotation process, flotation reagents such as lime, diced yellow sulphate, zinc sulphate and pine oil are reasonably added to preferentially float lead. Then flotation reagents such as butyl sulphate and copper sulphate are added to extract zinc. Then add sulfuric acid, butyl xanthate, pine oil and other flotation reagents to float sulfur. The grade of lead gold ore finally obtained is 75.79%, and the grade of zinc concentrate is 80.1%.
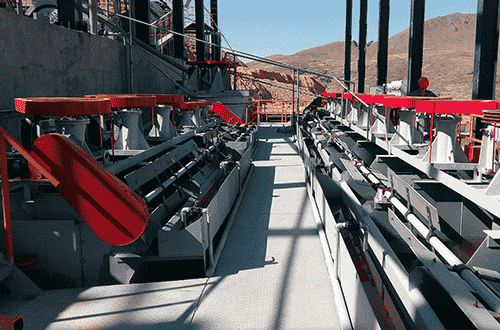
Zinc-Lead Sulphide Flotation Plant
Don't forget to share this post!

Flotation reagents refers to the agent that used in mineral flotation process, which can adjust the flotation behavior of minerals thus achieving a good effect of mineral separation...
 2019-03-15XinHai Views
2019-03-15XinHai ViewsFlotation frothers, also known as flotation foaming agent, is an essential flotation agent for froth flotation. The role of flotation frothers is mainly to produce a large amount of foam in the pulp...
 2019-05-15XinHai Views
2019-05-15XinHai ViewsXanthate, as the flotation collector with strong collection effect, is mainly used to enhance the hydrophobicity of the mineral surface to meet the requirements of flotation...
 2019-04-11XinHai Views
2019-04-11XinHai ViewsTOP